Google News: It’s Easy To Mess Up A Site Revamp

Google’s John Mueller answered a question about the SEO effects from making user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) changes to a website, advising that it’s better to plan in advance because it takes longer to fix problems if the changes break the SEO. The UI and UX are major elements of a website that affect how easy it is for site visitors to accomplish what they are there for, ultimately affecting user satisfaction. User Interface elements affect how site visitors interact with a website such as navigational, input forms, and informational icons. UX Considerations for any Website Update The online SEO blog, Search Engine Journal is reporting that user experience elements are a wider range of considerations that relate to accessibility, consistency in design, mobile responsiveness, readability, site speed, usability, and many other elements that in a well considered design have a positive impact on user satisfaction. This can affect SEO ranking from technical issues related to how Google crawls the page to on-page ranking considerations such as how content is displayed and consequently understood on a webpage. Making sitewide changes to the UI and UX changes, in addition to adding new webpages, is a majorundertaking and should not be considered lightly. Google’s John Mueller read the submitted question: “Anjaney asks: We’re preparing to launch a new website design for my company, involving UI/UX improvements and new pages. Is it better to change the page design one at a time?” Mueller answered: “One complexity is that a relaunch can mean so many different things, from just shifting a website to a new server and leaving everything else the same, to changing domain names and all of the content as well. First, you need to be absolutely clear what’s changing on the website. Ideally map out all changes in a document, and annotate which ones might have SEO implications. If you’re changing URLs, we have some great guidance on handling site migrations in our documentation. If you’re changing the content or the UI, of course that will affect SEO too. If you’re unsure about the effects, I’d strongly recommend getting help from someone more experienced – it’s easy to mess up a bigger revamp or migration in terms of SEO, if it’s done without proper preparation. Even with everything done properly, I get nervous when I see them being done. Fixing a broken migration will take much more time and effort than preparing well. In any case, good luck!” Plan Before Making Changes As Mueller recommends, it’s wise to create a plan for how the changes will roll out. Of particular importance is to document the state of the website before any changes are made, create a backup and use a staging environment. 1 – Crawl The Website An important thing to do prior to making major changes to a website is to crawl it with an app like Screaming Frog. Crawl the website in the original form and then crawl the updated version (preferably before it goes live). The crawl data can be used to identify a range of possible issues that can be fixed before the site goes live. Things that can be checked: >>> Spot missing pages >>> Catch misconfigured links >>> Missing meta and title elements >>> Review changes to linking patterns >>> Catch 404 errors >>> Check that 301 redirects are in place and properly functioning pages 2 – Create A Backup Of The Website Always have multiple backups of a website. There are so many things that can go wrong with a website backup. I’ve learned the hard way to have multiple redundant backups. For example, a consultant who was working on my server downloaded the images using the wrong transfer type, corrupting hundreds of thousands of images. Fortunately, I had backups on my desktop and duplicate backups on the server itself, so the images could be recovered. I have over 20 years of experience managing my own websites and dealing with client websites. The value of making multiple backups, including backups of backups stored on separate media, cannot be overstated. 3 – Stage The Website It’s a best practice to stage the new website so that any changes can be reviewed before they make it to the live server. The live version of a site is referred to as the production environment and the non-live duplicate version is called the staging environment. Website staging refers to the best practice of creating a duplicate version of a website (also known as a “staging environment”). Ideally the staging environment is on a separate server or at least on a separate location on the server so that there is no chance of changes on the staging environment accidentally making it to the live (production environment). The staging environment is used for development and quality assurance testing before changes are implemented on the live website. The main goal of staging a website staging is to identify and fix issues, technical bugs, or errors before they are carried over to the live version of the website (the production environment).
Skyscraper Technique & Link Building

The Skyscraper technique is a potent strategy in the realm of SEO and link building. It’s a methodology popularised by Brian Dean of Backlinko that involves creating superior content by improving upon existing content and then actively promoting it to secure high-quality backlinks. This technique has been widely embraced for its efficacy in enhancing search rankings and driving organic traffic. Let’s delve into the intricacies of the Skyscraper technique. Understanding the Skyscraper Technique The foundation of the Skyscraper technique lies in three fundamental steps: research, creation, and promotion. 1. Research: The initial phase involves meticulous research to identify content that performs well in your niche. This involves scouting for top-ranking content, analyzing its structure, comprehending its strengths and weaknesses, and identifying areas for improvement. Tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz can be incredibly helpful in this phase. The goal here is not just to replicate but to innovate and improve upon the existing content. 2. Creation: The next step is crafting content that surpasses what’s currently available. This involves adding more depth, incorporating updated information, enhancing visuals, infusing creativity, or presenting information in a more engaging manner. The objective is to create an exceptional piece of content that becomes the go-to resource in your niche. 3. Promotion: Creating stellar content is only half the battle; the other half is promoting it vigorously. Outreach is crucial here. Engage with influencers, relevant websites, bloggers, and journalists in your industry. Personalized outreach emails, guest posting, social media promotion, and networking are powerful tools in your arsenal. The aim is to get high-quality backlinks from authoritative sites that lend credibility to your content. Benefits of the Skyscraper Technique: 1. Enhanced Authority and Credibility: By producing superior content and securing high-quality backlinks, your website gains authority in the eyes of search engines and users. This, in turn, boosts credibility and trust, which are crucial for better search rankings. 2. Increased Organic Traffic: Higher search rankings and improved visibility lead to increased organic traffic. As your content gains traction, it becomes a magnet for visitors seeking valuable information, resulting in sustained traffic growth. 3. Long-term Results: The Skyscraper technique isn’t a short-term fix; it’s a sustainable approach that can yield long-term results. High-quality content tends to maintain its relevance, attracting links and traffic over an extended period. Implementing the Skyscraper Technique: 1. Choose the Right Content: Identify content with potential for improvement or content gaps in your niche. Look for topics that are highly relevant, trending, or have a significant search volume. 2. Create Exceptional Content: Invest time and effort into crafting exceptional content. This could mean adding depth, incorporating multimedia elements, improving readability, or presenting data in a unique way. 3. Outreach and Promotion: Strategize your outreach efforts meticulously. Personalized emails, guest posting, social media promotion, and collaborations are effective ways to reach out to influencers and secure backlinks. Challenges and Considerations: 1. Time-Intensive Process: The Skyscraper technique demands dedication and patience. It involves extensive research, content creation, and proactive promotion, which can be time-consuming. 2. Competitive Landscape: In competitive niches, acquiring backlinks from authoritative sites might be more challenging. Persistence and creativity in outreach are crucial here. The Skyscraper technique is a potent strategy for SEO and link building that centers on creating exceptional content and actively promoting it to secure high-quality backlinks. Its effectiveness lies in elevating your content above the existing competition, establishing authority, and driving organic traffic to your website. While it requires dedication and effort, the long-term benefits it offers make it a worthwhile approach in the ever-evolving landscape of SEO.
SEO: Putting SEO Top of Your List

SEO & 2024: Putting SEO at the Top of Your to do List: The Ultimate Guide Digital marketing and Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) remain an indispensable strategy for businesses aiming to increase their online visibility and drive organic traffic to their websites. As we step into 2024, prioritising SEO in your marketing efforts is not just advisable — it’s essential. This guide will delve into the importance of SEO, the latest trends, and actionable steps to supercharge your SEO strategy for the year ahead. Why Prioritise SEO in 2024? 1. Enhanced Online Visibility and Brand Awareness SEO empowers your website to rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs). With the majority of online experiences starting with a search engine, securing a prominent position on SERPs ensures increased visibility and brand exposure. 2. Drive Quality Traffic and Leads By optimizing your website for relevant keywords and phrases, you attract users actively searching for products or services related to your business. This targeted traffic is more likely to convert into leads or customers, driving tangible business growth. 3. Adaptation to Search Engine Algorithm Changes Search engine algorithms frequently evolve. Staying updated with these changes and adjusting your SEO strategy accordingly is crucial to maintain and improve your rankings. Prioritizing SEO ensures your website remains competitive in the dynamic digital landscape. Latest Trends in SEO for 2024 1. User Experience (UX) and Core Web Vitals Google’s emphasis on user-centric metrics, such as Core Web Vitals, highlights the significance of a seamless and enjoyable user experience. Prioritize factors like page speed, mobile responsiveness, and intuitive navigation to enhance UX and satisfy search engine criteria. 2. E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) Establishing your website as a credible source within your industry is vital. Focus on creating high-quality, authoritative content that reflects expertise and trustworthiness. Encourage user engagement and feedback to bolster credibility. 3. Voice Search Optimisation With the rise of voice assistants and smart devices, optimizing for voice search is gaining prominence. Incorporate conversational keywords and long-tail phrases into your content to cater to voice search queries effectively. 4. Video SEO Video content continues to dominate online platforms. Utilize video SEO techniques by optimizing titles, descriptions, and tags, enabling search engines to index and rank your video content for relevant queries. Actionable Steps to Boost Your SEO Strategy 1. Conduct a Comprehensive SEO Audit Start by evaluating your website’s current SEO performance with an SEO Audit. Identify technical issues, keyword gaps, and opportunities for improvement. Tools like Google Analytics and and SEO audit can provide valuable insights. 2. Keyword Research and Optimisation Perform keyword research to identify relevant terms and phrases your target audience uses. Optimize your website’s content, including titles, meta descriptions, headings, and body text, with these keywords strategically. 3. Mobile Optimisation Ensure your website is mobile-friendly and responsive. Given the increasing reliance on mobile devices for internet browsing, optimizing for mobile is crucial for SEO success. 4. Create High-Quality, Engaging Content Develop compelling and informative content that adds value to your audience. Incorporate multimedia elements, infographics, and videos to diversify your content strategy and enhance engagement. 5. Build Quality Backlinks Earn authoritative backlinks from reputable websites within your industry. Focus on natural link-building strategies, such as guest blogging, influencer collaborations, and creating shareable content to attract backlinks organically. 6. Monitor and Adapt Regularly monitor your SEO performance using analytics tools. Track keyword rankings, website traffic, and user behavior to identify areas for improvement. Be flexible and adapt your strategy based on data-driven insights. Putting SEO at the Top of Your 2024 to do List As we navigate the complexities of the digital sphere in 2024, SEO remains a cornerstone of successful online marketing strategies. By prioritising SEO and staying abreast of the latest trends and best practices, businesses can elevate their online visibility, attract quality traffic, and ultimately drive sustainable growth. Implementing a robust SEO strategy should undoubtedly top your to-do list for the year ahead, paving the way for long-term success in the competitive online landscape.
E-E-A-T: Expertise, Experience, Authority, and Trustworthiness

The Increasing importance of E-E-A-T If you want Google to pick your pages for SGE snippets, you need to create authoritative content, and authority is signalized by E-E-A-T — Expertise, Experience, Authority, and Trustworthiness. Numerous elements play into E-A-T signals, such as the expertise of authors, credible backlinks from sources like Wikipedia or niche-specific websites, and endorsements from industry experts and influencers. Specifically, in the realm of cooking and restaurants, acknowledgments from eateries, food bloggers, and renowned chefs—both locally and globally—contribute significantly to enhancing your site’s E-A-T. However, be ready that the pursuit of higher SERP rankings through E-E-A-T signals will ultimately drive up the cost of SEO services because: >>> Articles by expert authors will become more expensive; >>> Link-building services like outreach will cost more; >>> Authoritative media will increase the price for paid posts. How to stand out in a human first Google? Ensure that your content is not purely automated: Authenticity over Automation: Ensure your content isn’t solely generated by machines. Inject a human touch into your writing, making it relatable, engaging, and genuine. Balanced Automation with Validation: If you’re using automation tools, employ them judiciously. Validate the output to ensure accuracy, relevance, and coherence. Human oversight is crucial for refining automated content. Human Expertise and Insights: Incorporate insights from subject matter experts. Their unique perspectives elevate the content, adding depth and credibility. Authentic expertise can’t be replicated by algorithms. Uniqueness and Insightfulness: Strive for originality. Offer perspectives, analyses, or solutions that are distinct and thought-provoking. This distinctiveness captures attention in a sea of information. Interactive Engagement: Encourage dialogue and interaction. Engage with your audience, responding to queries or comments personally. Human interaction fosters a sense of community and trust. Ethical and Responsible Content: Be mindful of ethical considerations. Ensure your content is accurate, respectful, and aligns with ethical standards. Transparency and responsibility build credibility. Optimisation with a Human Touch: While optimising for search engines, maintain a balance. Prioritise readability and user experience. Keywords and algorithms matter, but readability and relevance to human readers are equally important. Remember, standing out in a human-centric digital landscape involves valuing authenticity, expertise, and genuine connections. Balancing automation with human insights ensures that your content resonates with your audience on a deeper level. Crafting Expertise, Experience, Authority, and Trustworthiness It’s important to be highly attentive and deliberate when crafting and advancing personal brands, especially for E-E-A-T development. In today’s landscape, it’s essential not only to hone professional skills but also to effectively broadcast them to both people and search engines. Active engagement within your niche through participation in conferences, interviews, podcasts, and public events can significantly boost your visibility and your brand’s standing. The same holds true for the personal brands of your content creators. Building a personal brand is a lengthy process, requiring considerable time and dedication. If managing your brand feels overwhelming, outsourcing expert content creation can be a viable solution. However, delaying this decision may lead to increased costs for outsourcing.
Google Local Search Ranking Factor

Recent findings by SEO professionals suggest that Google has recalibrated its local search algorithm, placing more emphasis on a business’s listed hours of operation as a key ranking signal. According to Joy Hawkins of Sterling Sky, the trend became noticeable after the November 2023 core update, leading to businesses that appear as closed being significantly less visible in local search results. Business Hours Confirmed As ‘Stronger’ Signal In Local Ranking Systems In response to the discussion, Google’s Search Liaison acknowledged the observations, confirming that “openness” has recently become a stronger signal for local search. “The team tells me we’ve long used “openness” as part of our local ranking systems, and it recently became a stronger signal for non-navigational queries. This might change in various ways, as we continue to evaluate the usefulness of it, however.” Non-Navigational Queries In Local Search? This confirmation led to more questions, starting with the definition of a non-navigational query. “If you were searching for a name of a business, that would generally be that you wanted to navigate / find that particular business. If you were searching for a general topic, that’s non-navigational.” Concerns About Business Response To ‘Openness’ Factor In another portion of the threaded discussion on X, Sherry Bonelli expressed concerns about an update that could prompt some businesses to falsely list 24/7 operating hours for the purpose of improving their local search visibility. This could lead to a poor user experience for searchers, as they may arrive at the business during non-operating hours. Google quickly addressed these concerns, advising against manipulating business hours because the ranking signal for openness is subject to ongoing adjustments. Plus, you could end up with a newly designed suspension email from Google. Best Practice: Keep Operational Hours Up-To-Date In Google Business Profiles Local businesses should maintain current business hours on Google Business Profiles – especially throughout the holiday – as it could influence local search visibility. For customers, maintaining accurate operational hours ensures minimal frustration during the final shopping days of the season. For businesses, it could increase visibility in the local pack rankings and attract more customers with near me searches, particularly if your competitors are closed.
Google’s VP: Google’s Index Size Revealed

Google’s Index Size Revealed by Google’s VP of Search Google rarely discusses the size of its web index—at least publicly. What exactly is Google’s index? Simply put, it’s a digital record of web pages and other documents eligible to be served in Google’s search results. If it’s not in the index, you won’t see it in search results. Google’s Index Size Revealed Many might believe you can simply search Google for any page on the web, but the opposite is actually more true. Out of trillions and trillions of possible pages, Google must narrow it down to mere “billions” of the most important documents. Google typically keeps the actual size of its index a secret, but recently, during testimony in the USA vs. Google antitrust trial, questioning by US attorneys revealed that Google maintained a web index of “about 400 billion documents.” The number came up during the cross-examination of Google’s VP of Search, Pandu Nayak. The 400 billion refers to Google’s index size in 2020. Nayak also testified that “for a time,” the index grew smaller than that. Finally, when asked if Google made any changes to its index capacity since 2020, Nayak replied “I don’t know in the past three years if there’s been a specific change in the size of the index.” The takeaway is that while 400 billion probably isn’t the exact index size, it’s most likely a good ballpark figure. Also, the size of the index shifts over time and may even be shrinking. How Big is 400 Billion Documents? Make no mistake, 400 billion is a big number. For example, the size of this (very small) website you are reading right now—Zyppy—is about 50 pages. So Google’s index could hold 8 billion websites like this one. Some sites are much larger. Wikipedia, for example, has 7 billion pages in Google’s index. So, Google could hold only about 50-60 Wikipedias. To put this figure in perspective, consider the size of Google’s index compared to popular indexes SEOs might know about – Ahrefs, Moz, and the Wayback Machine. And remember that Google, while it filters out a lot of junk, is more likely to contain vast numbers of documents like books, patents, pdfs, and scientific papers that serve smaller and more niche audiences. Google Excludes An Increasing Number of Documents Google can’t index every page it finds on the web. Nor does it want to. Google actually discovers trillions of pages while crawling. But as Nayak testified, most of those pages aren’t helpful to users. “Like I said, trillions of pages is a lot of pages. So it’s a little difficult to get an index of the whole web. It’s not even clear you want an index of the whole web, because the web has a lot of spam in it. So you want an index of sort of the useful parts of the web that would help users.” Beyond getting rid of spam, Nayak listed several other factors that impact the size of Google’s index: 1. Freshness Of Documents Some pages on the web change quickly – like the front page of CNN. Other important pages can stay the same for years. The challenge Google faces is estimating how often a page might change to keep its index fresh without unnecessary crawling. 2. Document Size Webpages are simply growing bigger. Ads, images, and more code mean the average size of web pages has grown huge over time. Since it costs money to crawl and process web documents, this creates a challenge for Google to index. “… over time at various times, the average size of documents has gone up for whatever reason. Webmasters have been creating larger and larger documents in various ways. And so for the same size of storage, you can index fewer documents, because each document has now become larger.” Bigger documents mean pressure to index fewer pages. 3. Metadata Storage Not only does Google store each document, it creates a tremendous amount of data about each document, including all the words and concepts related to each document. “… when we get these documents, not only do we create an index, we create a bunch of metadata associated with the document which reflects our understanding of the document. And that has also grown over time. And so that also takes space in the index. And as a result, that results in the number of documents that you can index in a fixed size of storage to go down.” As Google’s algorithms become more and more sophisticated, the amount of metadata increases, limiting the amount the index can grow in size. 4. Cost of indexing and processing At the end of the day, all those data centers cost a lot of money – and use a lot of electricity! “… there is this trade-off that we have in terms of amount of data that you use, the diminishing returns of the data, and the cost of processing the data. And so usually, there’s a sweet spot along the way where the value has started diminishing, the costs have gone up, and that’s where you would stop.” Takeaways for Web Publishers As AI-generated content floods the web as it becomes cheaper to produce, Google may be forced to index an increasingly smaller percentage of all web pages it finds. As Nayak explained, the goal of Google’s index isn’t about making a complete record of all documents but indexing enough pages to satisfy users. “… making sure that when users come to us with queries, we want to make sure that we’ve indexed enough of the web so we can serve those queries. And so that’s why the index is such a crucial piece of the puzzle.” This supports what Google has been publicly hinting at for years: Sometimes when Google doesn’t index a page, it does so because it doesn’t believe it’ll be useful to users. If Google isn’t indexing your pages, you may need to evaluate your site’s technical SEO, the usefulness
Google: High Quality Content

Google: Fix Technical Issues Before Chasing The ‘Next Big Thing’ Technical SEO basics and high-quality, helpful content should come before chasing SEO trends, say Google’s Search Relations team. In Search Engine Optimisation (SEO), where the focus often swings toward the latest trends and advanced tactics, Google’s Search Off The Record podcast team recently reminded everyone to get the basics right first. Martin Splitt, Gary Illyes, and John Mueller of Google’s Search Relations team explained that many websites still need help with basic technical SEO issues like site crawlability, indexing, and page rendering. These foundational factors directly impact a site’s performance in search results. As such, they should be addressed before less critical optimizations. Technical SEO: Foundation Before Innovation Technical SEO involves optimizing a website’s architecture and infrastructure to improve crawling and indexing by search engines. Unlike content creation or promotion, technical SEO focuses solely on the behind-the-scenes elements of a site. Illyes explains why he often posts on social media about technical SEO: “I like to post about technical things…because every now and then we notice that big site owners or big site SEOs will miss critical basic things.” Illyes described his observations from conferences where attendees were captivated by the ‘next big thing.’ He argued: “Just make sure your content is good first… looking at these websites that people put there, they are not helpful or useful to me as a user trying to find things.” Further, he underlined the significance of technical aspects in SEO, saying: “If Googlebot cannot reach your site, or rendering fails miserably, or there are no tokens (words) on the site or a page, then there’s not that much that Google can do for you.” Splitt agreed, stating technical SEO “is still important – it’s like all of those basics.” He suggested troubleshooting with a site’s homepage, as search engines view this as the most vital page. When these technical aspects are neglected, it may lead to critical issues, such as rendering failures or inaccessible sites, which can severely affect a website’s performance in search engine rankings. Quality Over Quantity: Rethinking Traffic Metrics Another key discussion point was the evaluation of content and the common misperception that high traffic equates to high-quality pages. Mueller cautioned relying solely on analytics without considering user experience: “I sometimes feel it’s misleading to just purely focus on the traffic.” He recounted an example of a site ranking well for generic keywords but providing little value to users. When traffic from those low-quality keywords declined, the aggregate stats looked concerning – but the loss was irrelevant. What Should You Pay Attention To? The hosts emphasized that metrics beyond traffic, such as user engagement and satisfaction, are more accurate indicators of a page’s usefulness and quality. Mueller states: “You almost need to look at the bigger picture of all of the traffic that’s gone, but also keep in mind… a lot of this was useless.” He encourages focusing on relevant queries and tracking lower-level pages to understand a site’s performance better. How To Create High-Quality Content? It’s not enough to churn out a high content volume; the content must serve a purpose and provide value to its intended audience. However, Illyes suggests that creating high-quality content might be more straightforward than most people think. The key is to focus on what will help people achieve their goals when they visit the page. This could mean providing comprehensive answers to common questions, solving problems, or sharing engaging and entertaining stories. Illyes states: “What if quality is actually simpler than most people think? What if it’s about writing the thing that will help people achieve whatever they need to achieve when they come to the page?” This discussion between Google’s Search Relations team emphasizes two key takeaways. (1) First, mastering the basics of technical SEO is essential before delving into advanced tactics. (2) Second, the quality of content and user engagement are more important than mere traffic numbers for evaluating a site’s success. They advised that websites can significantly improve SEO performance by focusing on these areas. Article Source: Search Engine Journal
Harnessing the Power of Internal Links
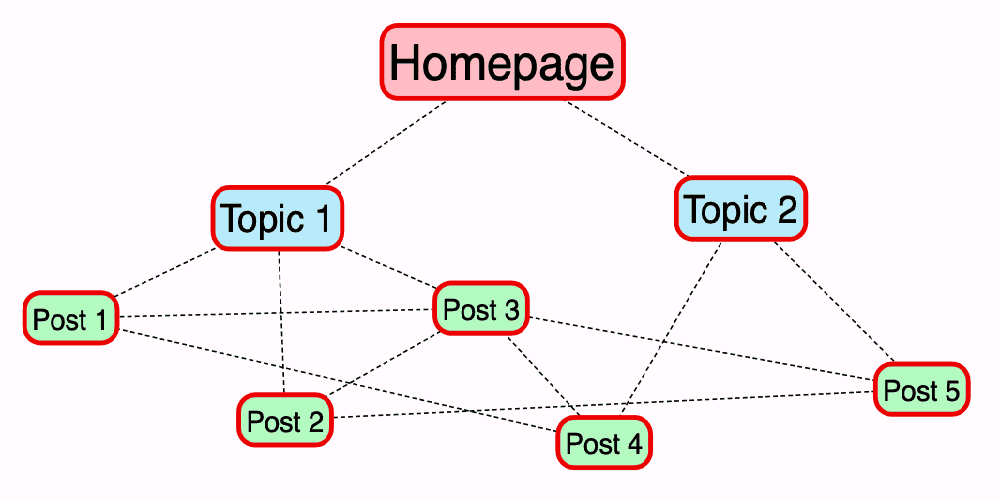
Maximizing SEO Potential: Harnessing the Power of Internal Links In the fast-paced world of digital marketing, staying ahead in search engine optimization (SEO) is key to boosting your online visibility. While external links often take the spotlight, internal linking is an underrated strategy that can significantly enhance your SEO efforts. Leveraging internal links strategically within your website not only aids in navigation but also plays a pivotal role in elevating your site’s ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). Understanding the Power of Internal Links Internal linking involves connecting different pages within your website using hyperlinks. These links guide users and search engine crawlers from one page to another, creating a web of interconnected content. When implemented effectively, internal linking can: 1. Improve Website Navigation: Internal links create pathways for visitors to explore your site, reducing bounce rates and increasing engagement. When users find relevant content easily, they tend to spend more time on your site, signaling its value to search engines. 2. Distribute Page Authority: By linking from high-authority pages to those needing a boost, you can spread the SEO value across your website. This helps in establishing a hierarchy of importance, allowing search engines to recognise key pages. 3. Enhance Keyword Optimisation: Strategic placement of internal links with relevant anchor text improves keyword association, signaling to search engines the relevance and context of linked pages. 4. Facilitate Indexing and Crawling: Search engine bots use internal links to navigate and index your site. Properly structured internal links make it easier for these bots to crawl and understand the content on your website, potentially leading to better rankings. Best Practices for Effective Internal Linking 1. Use Descriptive Anchor Text: Opt for descriptive and relevant anchor text that provides a clear idea of the linked page’s content. This helps both users and search engines understand the context. 2. Focus on Relevance: Link related pages together to guide users through a logical path of information. Ensure that the linked content adds value and context to the reader’s journey. 3. Maintain a Balanced Structure: Avoid overloading pages with excessive internal links as it may confuse both users and search engines. Keep it natural and user-friendly. 4. Regularly Audit and Update Links: Periodically review and update internal links to ensure they remain relevant and functional. Fix broken or outdated links to maintain a seamless user experience. 5. Utilize Site Architecture: Leverage site architecture to create a logical hierarchy and establish a strong internal linking structure. This helps search engines understand the importance of different pages. In the intricate landscape of SEO, internal linking stands as a powerful yet often overlooked tool. When used thoughtfully, it not only enhances user experience but also contributes significantly to your website’s search engine visibility. By incorporating internal links strategically and adhering to best practices, you pave the way for improved indexing, higher rankings, and ultimately, greater organic traffic. Unlock the true potential of your website’s SEO by weaving an interconnected web of internal links — it’s a digital pathway to heightened visibility and sustained success.
Google Rolls Out November 2023 Core Update

Google Rolls Out November 2023 Core Update Google begins rolling out the November 2023 core update, the second major change to its search algorithm in as many months. Google has released its November 2023 core update, the update is presently rolling out and expected to be fully implemented over the next few weeks. Core updates are periodic adjustments to the algorithms that power Google’s search results, which are designed to improve the relevance and quality of the web pages shown for search queries. “We have different systems that are considered core to our ranking process; this month’s core update involves an improvement to a different core system than last month,” Google said in a statement. “However, our guidance about core updates is the same for both.” This latest core update comes on the heels of Google’s October 2023 core update, released last month. While core updates typically happen every one to two months, it’s rare for two major updates to be released so close together. Google suggests that most website owners don’t need to make significant changes in response to core updates. “Chances are, there’s nothing to do for most creators who have already been working to create helpful, reliable, people-first content,” the company said. However, Google recommends reviewing its core update guidance in case traffic or rankings are impacted. Focusing on high-quality, useful content is always advisable. Google has published an updated Q&A addressing common questions about how search updates work. Here are some of the highlights: >>> Core updates are different from Google’s ranking systems. Updates adjust the algorithms while ranking systems generate the search results. >>> Thousands of updates happen per year, but only some notable ones are announced publicly. >>> If your site is affected by a core update, it doesn’t necessarily mean you’re being penalized for spam. Non-spam issues may be the cause. >>> Google tries to avoid releasing major updates during the busy holiday shopping season, but it’s not always feasible. >>> Google notes that you can post questions in the Google Search Central community forums if you see significant changes in your site’s performance around core update releases. The company’s search specialists monitor those forums to identify potential issues caused by the updates. The November 2023 core update marks the second major algorithm change in as many months. This is the fourth core update Google’s pushed out in 2023. Previous updates were released in March, August, and October, each involving multi-week rollouts.
Google Rollout of October 2023 Update

Google October 2023 Spam Update Google finished rolling out the October 2023 Spam Update targeting thin and misleading content. The spam-fighting update was first announced on October 4. In its announcement, Google says the latest spam update was initiated based on user feedback. Many people reported increased spam results when searching in their native languages. With this update to its spam detection capabilities, Google hopes to improve search results for users worldwide. October 2023 Spam Update Google utilizes automated systems and human reviewers to identify and demote spammy pages and sites, with one such system being SpamBrain, which leverages AI and machine learning to stay on top of emerging spam tactics. What Google Considers Spammy Or Misleading Google outlines prohibited practices in its spam policies documentation. Practices that Google considers spammy include: >>> Hidden text or links are invisible to users but visible to search engines. >>> Automatically generated content with little added value. >>> Large-scale, unpermitted article scraping. >>> Pages overloaded with distracting ads. >>> Thin affiliate content focused heavily on monetization. >>> “Doorway” pages and other attempts to trick search engines. >>> Aggressive or misleading commercial tactics like false claims. Google recommends that sites focus on providing a transparent, honest user experience. Those that do should fare well after spam updates. Impact On Websites Google’s latest spam update is a reminder to stay up-to-date on best practices with those sites negatively impacted, needing to review their content and SEO strategies. Check for thin affiliate pages, hidden text, scraped content, and excessive ads. Any tactics deemed overly promotional or misleading should be corrected. Lastly, stay current with Google’s guidelines and conduct regular website audits. Advice For Publishers As always, websites should focus on publishing high-quality content to avoid being impacted by Google’s spam updates. Practical, engaging, and original content is far less likely to be affected by algorithmic changes. Thin or duplicated content poses a much higher risk. Regularly monitoring backlinks and conducting website audits can help identify potential red flags. Take corrective actions promptly. Prioritising the user experience rather than shortcuts or tricks is the best path to staying in Google’s good graces. Focusing on value and transparency will serve websites well.
